In this post, I document the full formula assignment pipeline using MFAssignR, tailored for Orbitrap-MS data post-peak list processing (There is no need to reinvent the wheel here).
The steps include quality control filtering, noise estimation via Kendrick Mass Defect (KMD) plots, isotopic filtering, recalibrant inspection, and final formula assignment.
1. Load Input and Install Required Packages
1 | setwd("./output/ToF_peak_list/") |
2. Reading note: How MFAssignR filter raw peaks and assign formulas
Noise filtering
MFassignR uses a Kendrick Mass Defect (KMD)-based noise filtering approach (KMDNoise) before formula assignment. It analyzes raw spectra to identify background regions free from analyte signals. By slicing along two KMD lines (default intercepts: 0.05 and 0.2), it estimates the baseline noise level. Peaks below a user-defined signal-to-noise (SN) threshold (e.g., 3–10× noise) are removed. This enhances data quality by filtering out low-intensity noise and multiply charged ions.
Formula assignment
MFAssignR applies several non-optional quality assurance (QA) rules to screen out chemically invalid formulas during assignment. Below is a summary of key rules:
🔍 Fundamental Rules
| Rule | Description |
|---|---|
| Senior Rule (Kind & Fiehn, 2007) |
Ensures molecular formulas follow known valency and bonding constraints. Useful for identifying feasible adduct or fragment ions. |
| Nitrogen Rule | For odd vs even nominal masses: odd → odd number of N atoms. |
| Large Atom Rule | Large atoms tend to fragment at weak bonds; used to predict fragmentation patterns. |
| Max Hydrogen Rule | Limits H count based on allowed bonding from other atoms. Prevents over-saturation. |
| Max DBE Rule (Lobodin et al., 2012) |
Ensures formulas have chemically valid unsaturation: DBE = (2C + 2 + N − X − H)/2 |
3. Noise Estimation Using KMD
KMDNoise isolates low-intensity regions via Kendrick Mass Defect linear slice filtering:
1 | Noise <- KMDNoise(Data) |
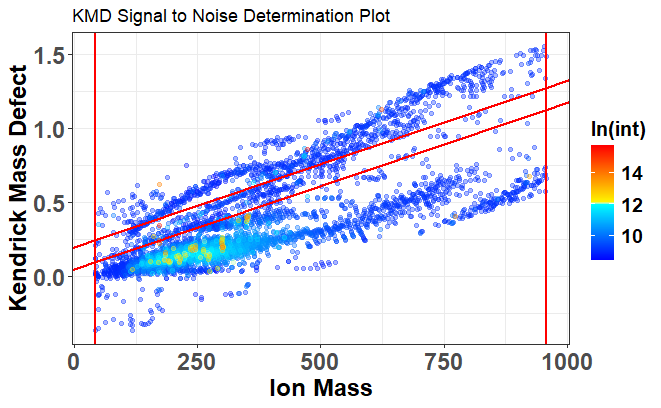
Signal-to-noise (S/N) plot
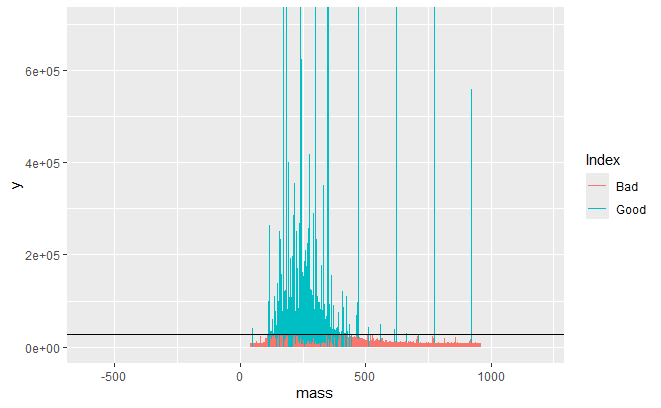
Spectrum after noise removal
4. Isotope Prescreening
1 | Isotope <- IsoFiltR(Data) |
5. Initial CHO Formula Assignment
1 | Assign <- MFAssignCHO(Mono, Iso, ionMode = "pos", lowMW =50, highMW = 1000, |
6. Review Assignment Quality
1 | Unambig1 <- Assign[["Unambig"]] |
7. Identify Recalibrant Series and Recalibrate
This step uses high-confidence assigned ions (from Unambig1) to refine m/z accuracy via internal recalibration.
1 | check <- RecalList(Unambig1) |
8. Final Formula Assignment with Extended Elements
1 | Assign <- MFAssign(Mono2, Iso2, ionMode = "pos", lowMW =50, highMW = 1000, |
A summary of the parameters used in the MFAssign function:
| Parameter | Value | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
Mono2 |
[input] | Dataframe of monoisotopic masses (from Recal step) |
Iso2 |
[input] | Dataframe of isotopic masses (from Recal step) |
ionMode |
"pos" |
Specifies positive ionization mode |
lowMW |
50 |
Lower limit of molecular mass to be assigned |
highMW |
1000 |
Upper limit of molecular mass to be assigned |
POEx |
0 |
Whether to allow odd-electron positive mode ions (0 = no) |
Zx |
1 |
Charge state allowed in formula assignment |
Mx |
2 |
Maximum number of sodium adducts (Na) allowed |
Ex |
0 |
Amount of 13C isotopes allowed |
Nx |
3 |
Maximum number of nitrogen atoms (14N) allowed |
Sx |
3 |
Maximum number of sulfur atoms (32S) allowed |
ppm_err |
20 |
Error tolerance for formula assignment in ppm |
H_Cmin |
0.3 |
Minimum hydrogen-to-carbon (H/C) ratio |
HetCut |
"off" |
Disable high heteroatom QA filter |
DeNovo |
300 |
Cutoff for de novo formula generation (masses above this value are not considered) |
NMScut |
"on" |
Enable nominal mass series QA check (Koch et al., 2007) |
SN |
0.25*KMDN |
Signal-to-noise threshold for formula assignment, scaled by KMD-based noise estimate |
9. Save Final Outputs
1 | Unambig2 <- Assign[["Unambig"]] |
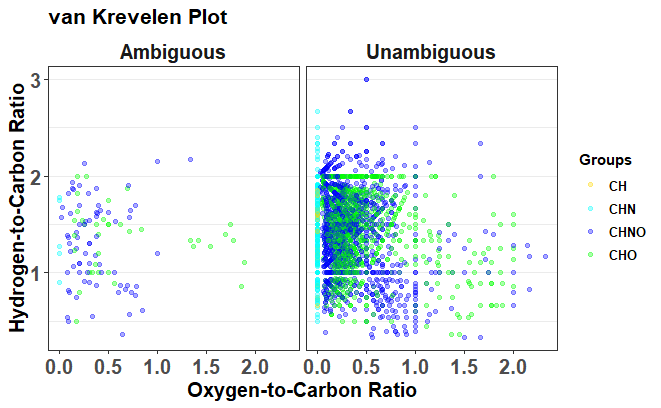
1 | input_name = './output/ToF_peak_list/20250731_Punjab_Orbitrap+TOF_peak_list' |
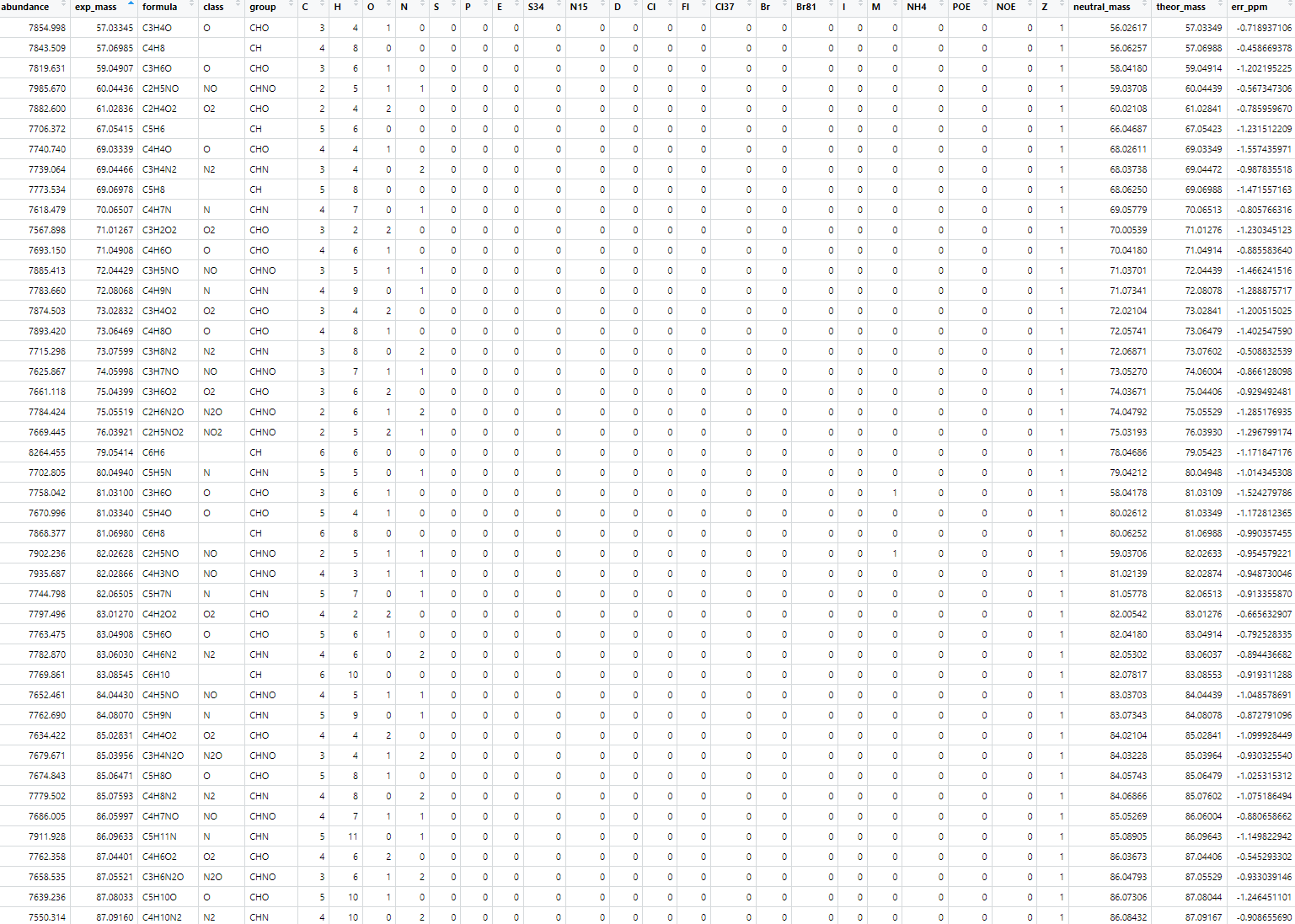
The assigned formula will be shown as:
Reference
- Kind, T. & Fiehn, O. (2007). Seven Golden Rules for heuristic filtering of molecular formulas obtained by accurate mass spectrometry. BMC Bioinformatics, 8, 105
- Schum, S.K., Brown, L.E., & Mazzoleni, L.R. (2020). MFAssignR: Molecular formula assignment software for ultrahigh resolution mass spectrometry analysis of environmental complex mixtures. Environmental Research, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.11011
- MFAssignR github page, https://github.com/skschum/MFAssignR
Comments